Let's see how the credit term of 2/10, n/30 works in an example Michael & Co Ltd ships $1,000 of goods to a customer If the customer pays Michael & Co Ltd within 10 days of the invoice date, the customer is allowed to deduct $ (2% of $1,000) from the purchase of $1,000Otherwise the fullundiscounted purchase price is due in 30 days This invoice agreement is usually written like 2/10, n/30 or 2/10, net/30 There are two ways to account for a cash discount the gross method and the net method Example Let's look at an example Assume Big Guitar, LLC buys $2,000 of inventory on January 1st with terms 2/10, n/30A company purchased $1,800 of merchandise on July 5 with terms 2/10, n/30 On July 7, it returned $0 worth of merchandise On July 28, it paid the full amount due Assuming the company uses a perpetual inventory system, and records purchases using the gross method, the correct journal entry to record the merchandise return on July 7 is Recording purchases returns
1
2/10 n/30 journal entry example
2/10 n/30 journal entry example-The journal entry to record the reimbursement of the fund on September 30 is debit petty cash $250, credit cash $250 Which of the following is an accounting method that (1) estimates and reports bad debts expense from credit sales during the period the sales are recorded, and (2) reports accounts receivable at the estimated amount of cash to be2/10 net 45 means 2% early payment discount within 10 days or total amount of invoice due in 45 days 3/10 net 30 means 3% early payment discount within 10 days or total amount due in 30 days 3/ net 60 means 3% early payment discount within days or total amount due in 60 days 2/EOM net 45 means 2% early payment discount if paid by the




Accounting For Merchandising Operations Ppt Download
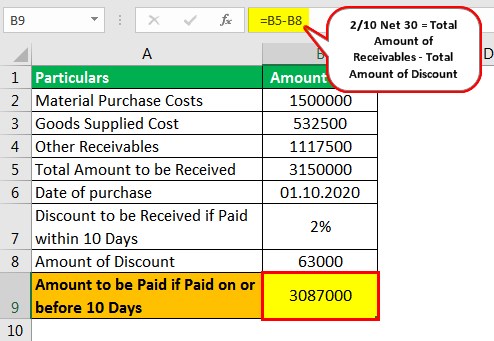
We can understand the order of input credit set off and its journal entries with an example Example – Month End Details (Total Balances) CGST Payable (Output) A/c – Rs 50,000 CGST Input Credit A/c – SGST Payable (Output) A/c – Rs 50,000 SGST Input Credit A/c IGST Payable (Output) A/c – Rs Sales Discount Example For example, if a business sells goods to the value of 2,000 on 25/10, n/30 terms, it means that the full amount is due within 30 days but a 25% sales discount can be taken if payment is made within 10 days The sales discount in this example is calculated as followsJournal Entry for Cash Discount 100 keyboards are sold for the invoice price of 300 each with payment terms 1/10, Net 30 days Journal entry for a cash discount, in this case, will depend on the terms that the buyer will get 1% cash discount from total invoice price if the payment is made within the first 10 days of receipt of the invoice (Assuming there is no trade discount)
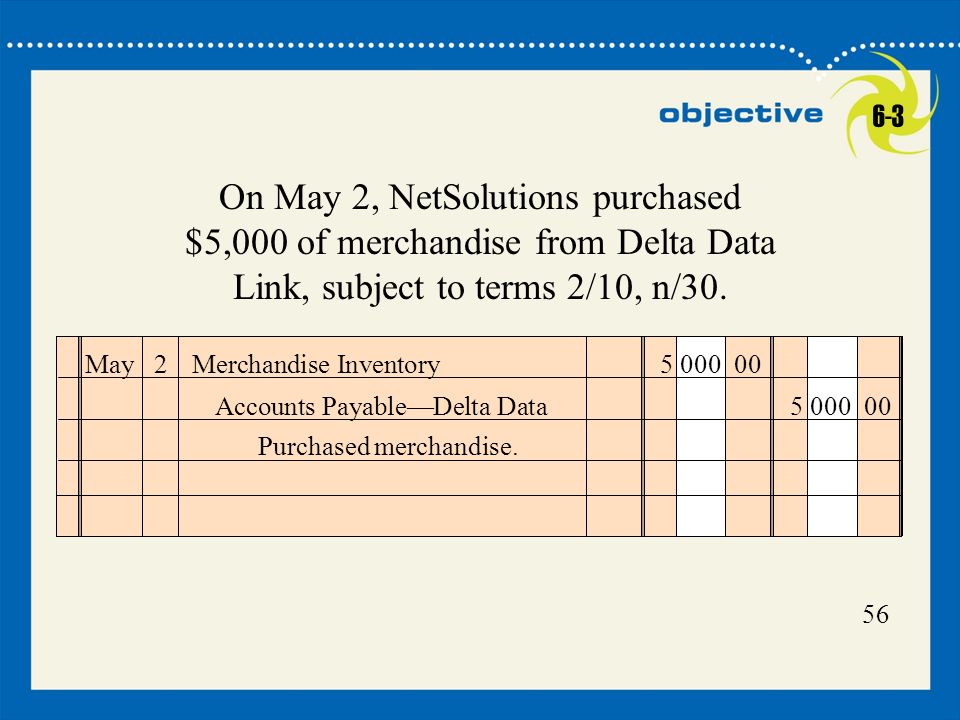
For example, the credit terms for credit sales may be 2/10, net 30 This means that the amount is due in 30 days (net 30) However, if the customer pays within 10 days, a Example Company A purchases $5000 in inventory from Company B Terms of the sale are 2/10 n/30 Within ten days Company A remits the invoice; A Journal Entry is simply a summary of the debits and credits of the transaction entry to the Journal Journal entries are important because they allow us to sort our transactions into manageable data You'll notice the above diagram shows the first step as "Source Documents" Source documents are things such as receipts, invoices, bank
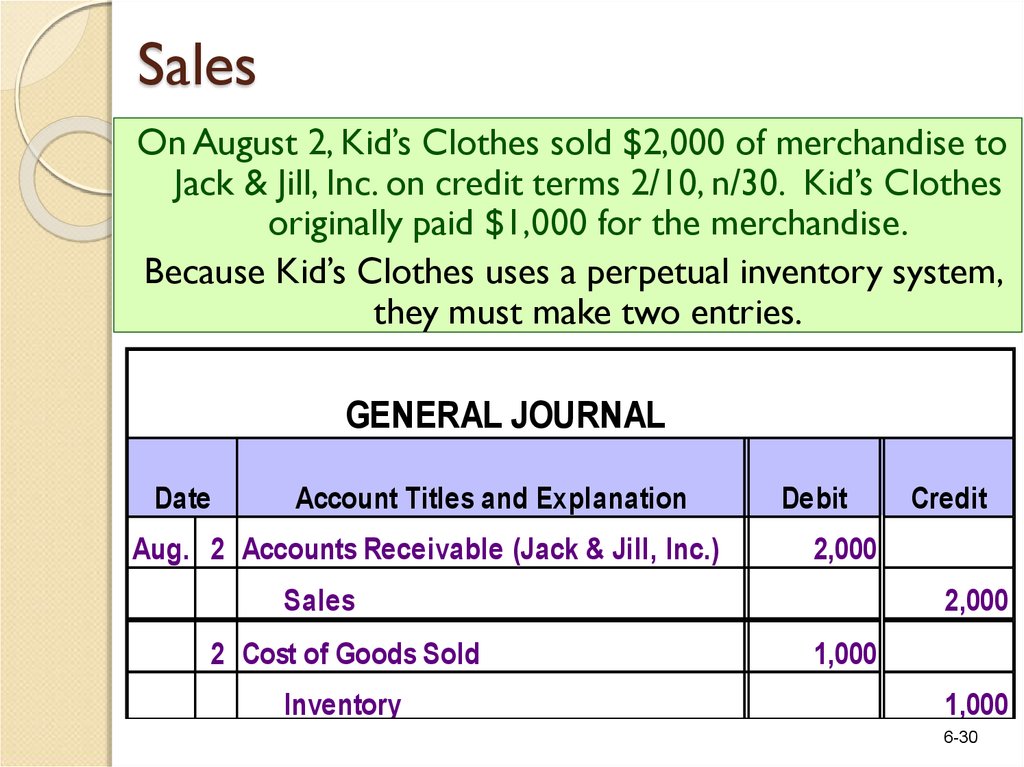
Generally take the form of 2/10, n/30 where 2 is the discount % 10 is the discount period in days n is the net (total) amount to pay the transaction requires two journal entries the first entry records the revenue from the sale at the selling price and the Example 2 $800 of inventory is sold on account, FOB shipping point TheRecord the journal entries for the following 1 Business started with cash 8,000 and plant & machinery 3,000 2 Stock purchase for sale (cash purchase) = 3,000, credit purchase = 5,000 3 Wages paid 1,000 (including ,000 relating to a future year) 4 Salaries paid 0,000 but due 110,000 5 Sales made for cash 600,000 and on creditSales Discount Transaction Journal Entries On August 1, a customer purchases 56 tablet computers on credit The payment terms are 2/10, n/30, and the invoice is dated August 1 The following entries occur On August 10, the customer pays




Fa 2 Module 6 Current Financial Assets And




Credit Terms Due Date Invoice Date Eom Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
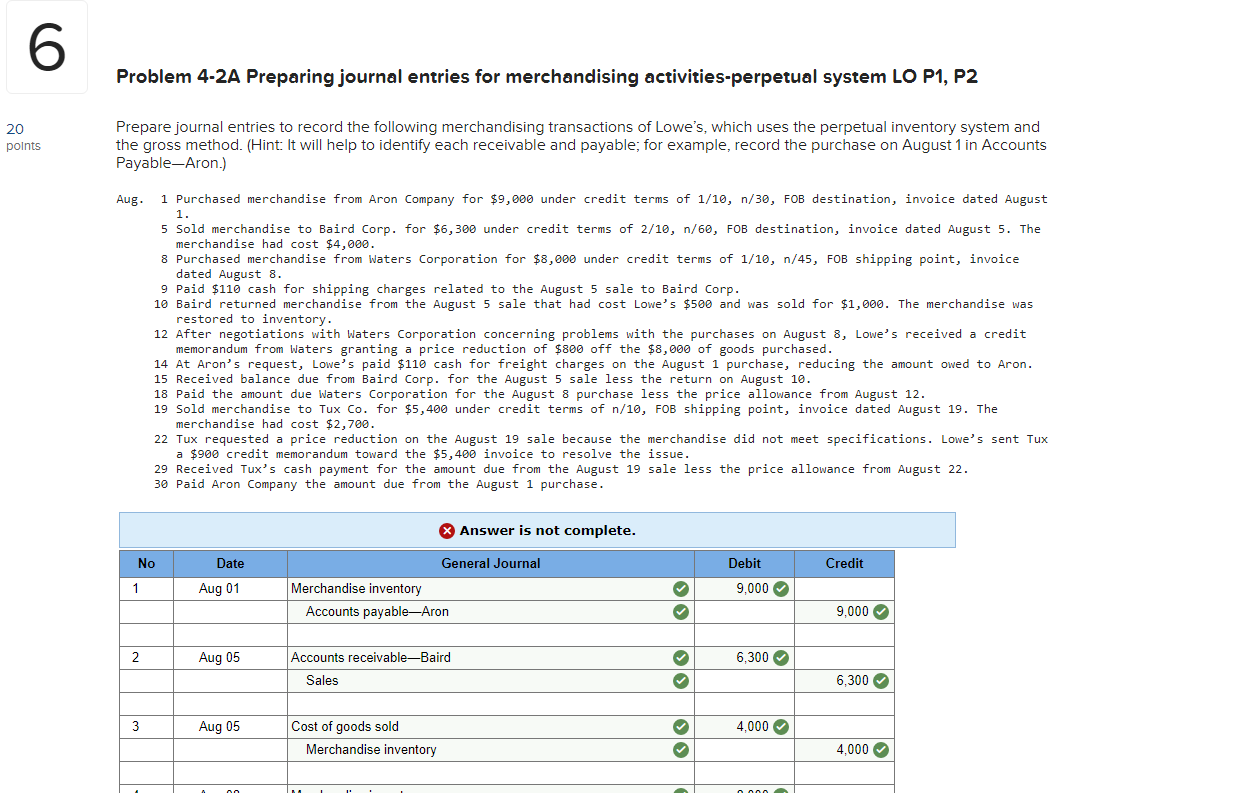
Debits must equal credits for each entry in a general journal After the entry is journalized, the equality of debits and credits is verified For this entry, the total debits, $10,, equal the total credits, $10, S T E P S Cash 10, Barbara Treviño, Capital 10,Hint It will help to identify each receivable and payable; Journal Entry Merchandise are purchased either for cash or on account The journal entries required to record the purchase of merchandise under both the cases are discussed below Example On 1 January 16, John Traders purchased merchandise for $15,000 in cash from Sam & Co The journal entry for this purchase is shown below




Chapter 6 Power Notes Accounting For Merchandising Businesses




Acg21 Connect Ch 4
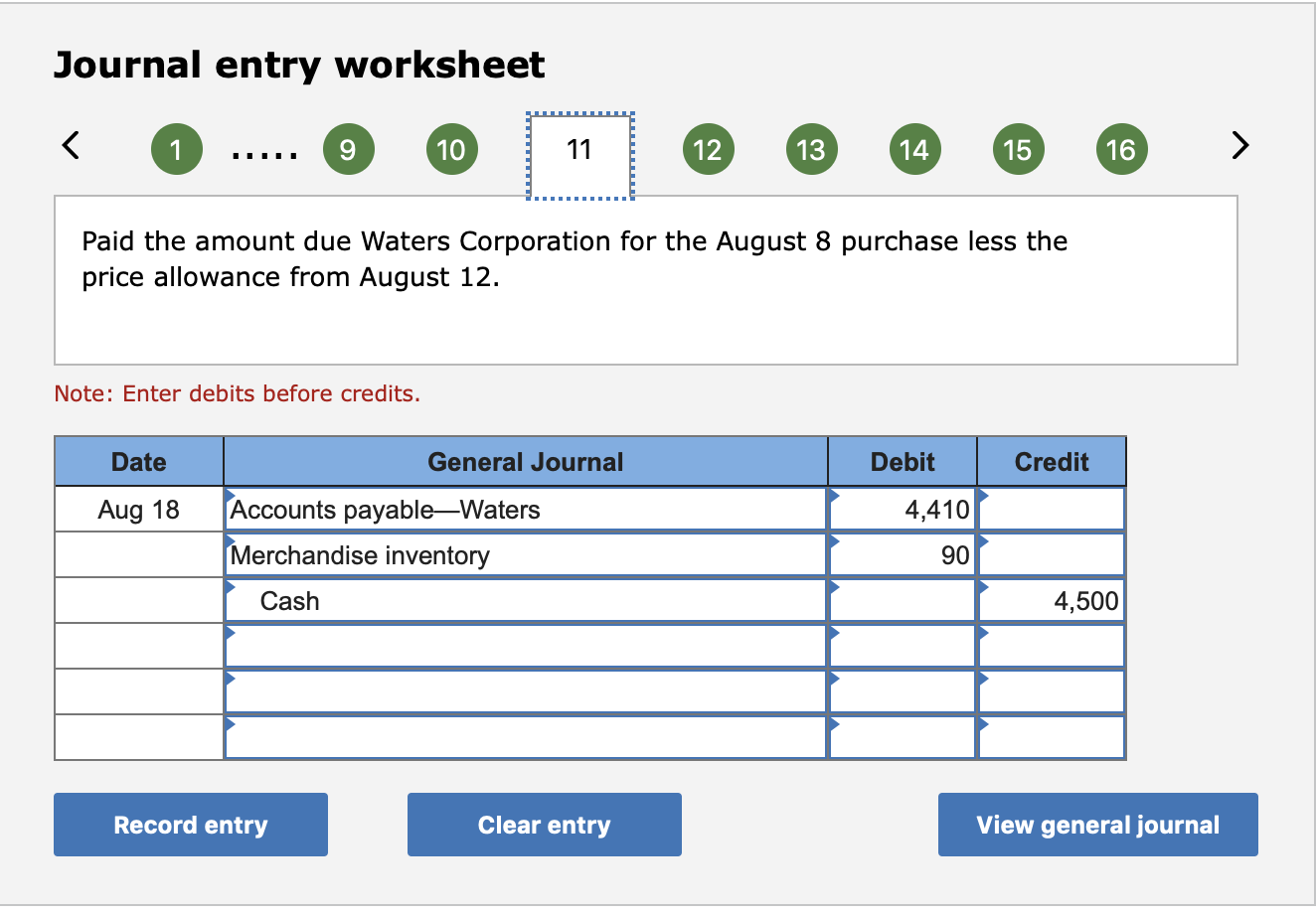
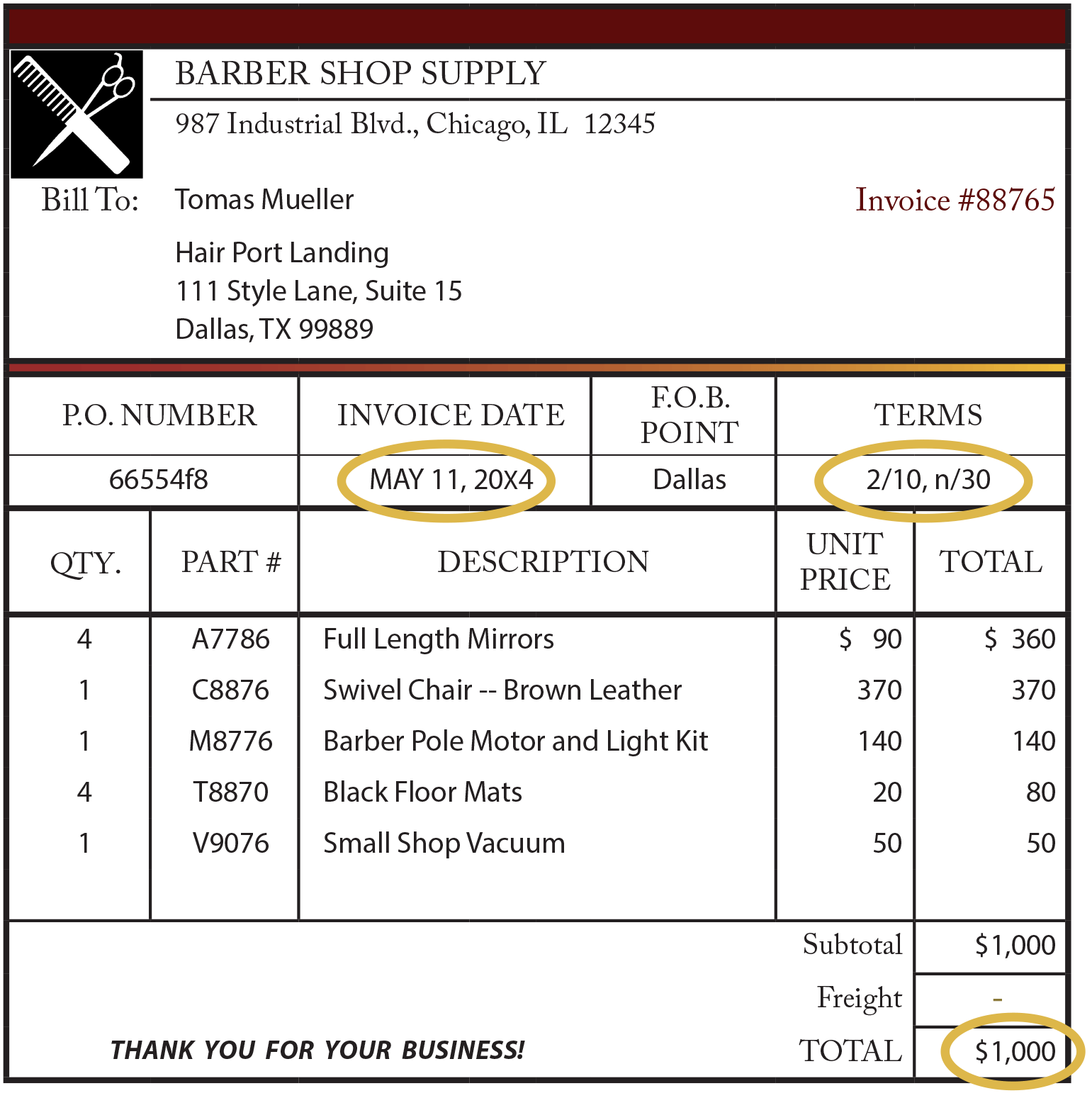
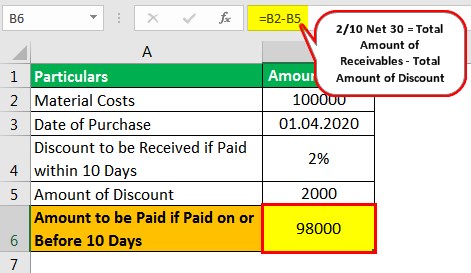
To illustrate 2/10, n/30, assume that a vendor's invoice for $1,000 is dated June 1 and the vendor has granted the buyer an allowance of $100 This means the net amount is $900 and that only $900 will be eligible for the early payment discountFor example, record the purchase on August 1 in Accounts PayableAron Aug 1 Purchased merchandise from Aron Company for $6,000 under credit terms of 1/10, n/30, FOB destination, invoice dated August 1 5 Sold merchandise to Baird Corp for $4,0 under credit terms of 2/10, n/60, FOB5/15 Debit Accounts Payable 27,000 Credit Cash 26,460 Merchandise Inventory 540 27,000 * 02 = $540 discount Purchase Returns & Purchase Allowances Examples On May 9th, company purchaed $,000 of merchandise inventory on account, credit terms 2/10,n/30




What Do Credit Terms 2 10 Net 30 Mean Planergy Software




Accounting For Merchandising Operations Ppt Download
2/10 n 30 journal entries vary depending on the accounting method used LIFO vs FIFO , accounting vs economic income , and many other matters make 2/10 n 30 accounting somewhat complicated Strong company policies must be in place to ensure smooth bookkeepingSales Discount Transaction Journal Entries On August 1, a customer purchases 56 tablet computers on credit Terms are 2/10, n/30, and invoice dated August 1 The following entries occur On August 10, the customer pays their account in full The following entry occursRecall from Merchandising Transactions, that credit terms of 2/10, n/30 signal the payment terms and discount, and FOB shipping point establishes the point of merchandise ownership, the responsibility during transit, and which entity pays shipping charges Therefore, 2/10, n/30 means Sierra Sports has ten days to pay its balance due to receive



Solved Prepare Journal Entries To Record The Following Chegg Com



The Merchandising Operation Sales Principlesofaccounting Com
Journal Entries Doubleentry bookkeeping, in accounting, is a system of bookkeeping so named because every entry to an account requires a corresponding and opposite entry to a different account This lesson will cover how to create journal entries from business transactions Journal entries are the way we capture the activity of our business It includes material cost, direct or services 2/10 net 30 means that if the amount due is paid within 10 days, the customer will enjoy a 2% discount Otherwise, the amount is due in full within 30 days Example of a Trade Credit The CEO CEO A CEO, short for Chief Executive Officer, is the highestranking individual in a company or organization The CEO is responsible for the Payroll journal entries are used to record the compensation paid to employees These entries are then incorporated into an entity's financial statements through the general ledger The key types of payroll journal entries are Initial recordation The primary payroll journal entry is for the initial recordation of a payroll



Appendix Analyze And Record Transactions For Merchandise Purchases And Sales Using The Periodic Inventory System Principles Of Accounting Volume 1 Financial Accounting
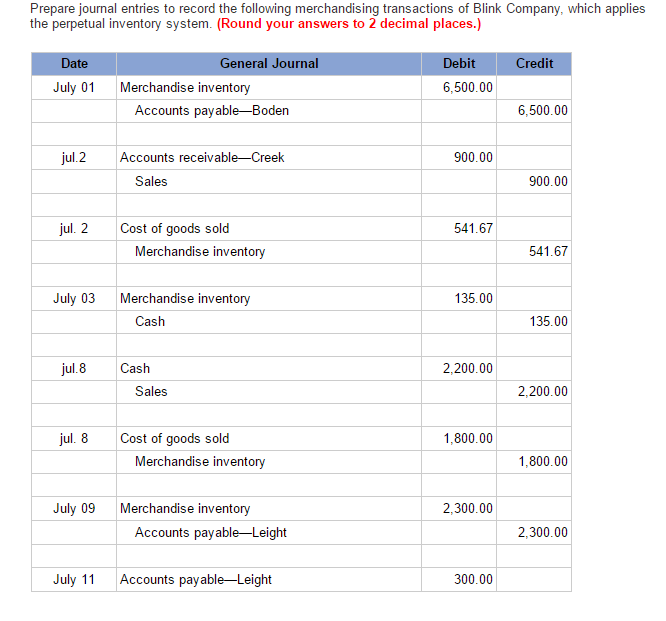



Solved July 1 Purchased Merchandise From Boden Company For Chegg Com
$5000 less 2% equals $4900Transcribed image text Knowledge Check 01 A seller uses a perpetual inventory system, and on April 4, it sells $5,000 in merchandise (its cost is $2,400) to a customer on credit terms of 3/10, n/30 Complete the two journal entries to record the sales transaction by selecting the account names from the dropdown menus and entering the dollar amounts in the debit or credit columns The percentage of cash discount is mentioned in payment terms For example, the terms 2/10, n/30 means a 2% discount will be allowed if the payment is made within 10 days of the date of invoice, otherwise, the full amount is to be paid in 30 days Journal Entry for Cash Discount Cash discount is an expense for seller and income for buyer It is, therefore, debited in the books




Solved Use The Provided Chart Of Account To Prepare The Chegg Com




Glo4 01 Based On Problem 4 1a Cabela 39 S Company Lo P1 P2 Prepare Journal Entries To Record Homeworklib
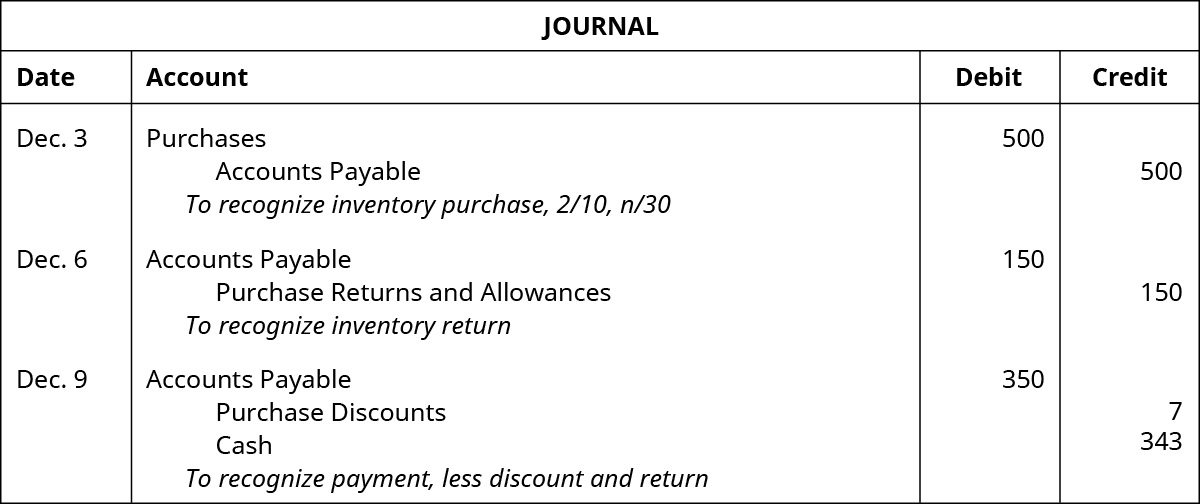
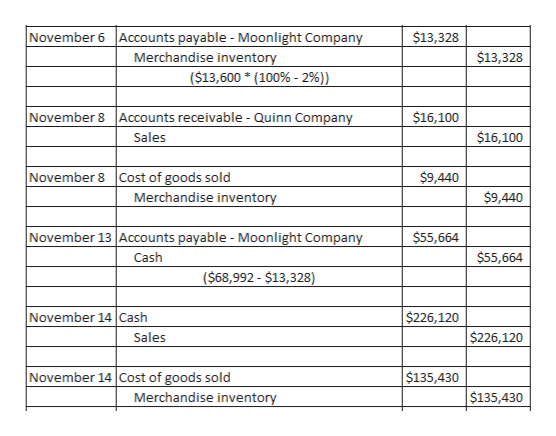
2/10 Net 30 Example See Also 2/10 net 30 2/10 Net 30 Example Mary has started a processing plant for natural vegan snacks In her business, equipment does all of the heavy lifting that human resources can not Mary has purchased many pieces of equipment One of these is a large oven to bake her healthy snacks in2 Example Prepare journal entries to record the following transactions entered into by the Castagno Company Nov 1 Sold merchandise on account to Mercer, Inc, for $18,000, terms 2/10, n/30 Nov 5 Mercer, Inc, returned merchandise worth $1,000 Nov 9 Received payment in full from Mercer, Inc Date Debit Credit2/10, n/30 means that customers will receive 2% discount if they settle accounts receivable within 10 days after the invoice date Customers have 30 days to settle the invoice, however, they will not receive discount if they pay after 10 th day of invoice date Payment term mean 2/10, n/30 or



Sales Journal Explanation Format Example Accounting For Management




Mastering Inventory
Basics of Journal Entries Accounting Journal Entry Examples More Examples of Journal Entries Accounting Equation Double Entry Recording of Accounting Transactions Debit Accounts Credit Accounts Intangibles Other than Goodwill InternalUse Software Website Development Costs 360 Property, Plant and Equipment Example of a Cost of Goods Sold Journal Entry Simple version ABC International has a beginning balance in its inventory asset account of $500,000 It buys $450,000 of materials from suppliers during the month At monthend, it counts its ending inventory and determines that there is $0,000 of inventory on hand The cost of goods sold Net 30 terms or n/30 means that payment in full is due 30 days after the date of the invoice Net 30 terms are often combined with a cash discount for early settlement For example 2% 10 days, net 30 terms or 2/10, n/30 means, that a 2% discount can be taken if payment is made with 10 days, otherwise the full amount is due within 30 days




Accounts Receivable Wikipedia



Accounting For Merchandising Businesses Ppt Download
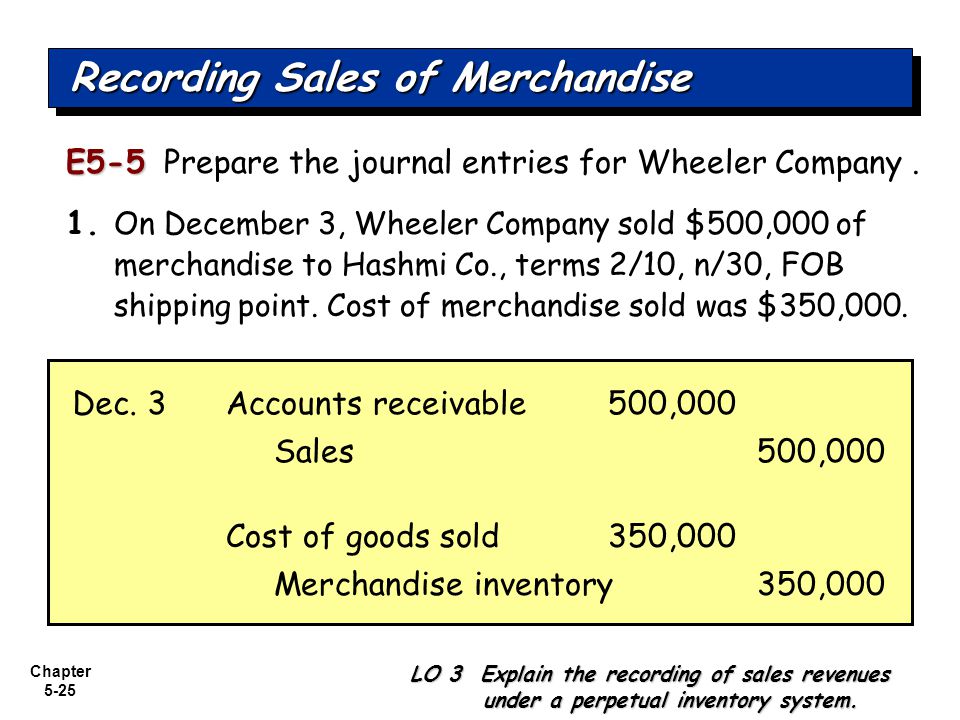
Q1 The entity sold merchandise at the sale price of $50,000 in cash The cost of merchandise sold was $30,000 Prepare a journal entry to record this transaction Journal Entry When merchandise is sold, two journal entries are recordedExample Credit terms may read 2/10, n/30 LO 2 Explain the recording of purchases under a perpetual inventory system Recording Purchases of Merchandise 5 2% discount if paid within 10 days, otherwise net amount due within 30 days 1% discount if paid within first 10 days of next month 2/10, n/30 1/10 EOM Net amount due within the first 10Problems 2 Prepare general journal entries for the following transactions of a business called Pose for Pics in 16 Aug 1 Hashim Khan, the owner, invested Rs 57,500 cash and Rs 32,500 of photography equipment in the business 04 Paid Rs 3,000 cash for an insurance policy covering the next 24 months 07 Services are performed and clients are billed for Rs 10,000



1




Lesson 7 9 Journal Entries Net Method Patrick Lee Msa
Sales Discount Transaction Journal Entries On August 1, a customer purchases 56 tablet computers on credit The payment terms are 2/10, n/30, and the invoice is dated August 1 The following entries occur On August 10, the customer paysAccounts Payable Journal Entries – Example #2 During February 19, the Midterm international ltd did the transactions, as mentioned below The company uses the periodic inventory system, and to account the discounts, the company uses the gross method Feb 02 Company purchased the inventory worth $ 50,000 with terms 2/10, n/30, FOB The following journal entry would be made in the books of Metro company to record the purchase of merchandise * Net of discount ($500 × 15) – $25 discount (2) On the same day, Metro company pays $3 for freight and $100 for insurance The following journal entry would be made to record the payment of freightin and insurance expenses (3)




Acct 1 Midterm Flashcards Quizlet




What Is The Net Method Definition Meaning Example



Appendix G Subsidiary Ledgers And Special Journals Available At Www Wiley Com College Weygandt




Prepare Journal Entries To Record The Following Merchandising Transactions Of Cabela S Which Uses The Perpetual Inventory Homeworklib




Accounts Payable Explanation Journal Entries Examples Accounting For Management




Chapter 7 Inventory Learning Objective 1 Identify What



2 10 Net 30 Meaning Examples Advantages Disadvantages




Analyze Journalize And Report Current Liabilities Principles Of Accounting Volume 1 Financial Accounting




Points General Journal Debit Credit 10 Out Of Pdf Free Download




Acct 2301 Exam 2 V2 Key Doc



Merchandising Activities Prezentaciya Onlajn



Accounts Payable Vs Accounts Receivable Overview Examples



2
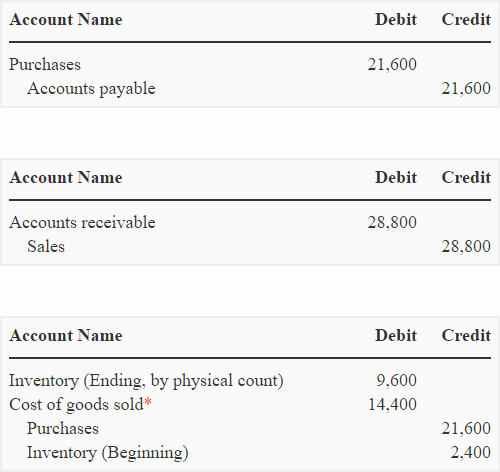



Periodic Inventory System Explanation Journal Entries Example Accounting For Management




Buyer Entries Under Perpetual Method Financial Accounting




Tutorial 1
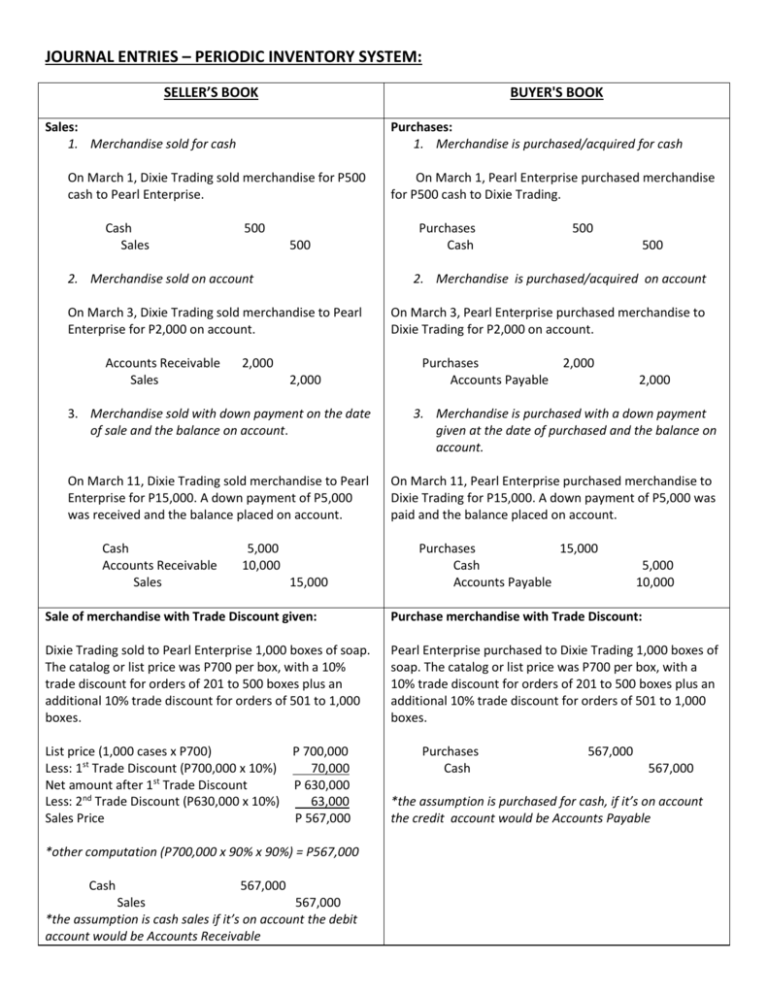



Illustrative Example Journal Entries For New Accounts



2




Sales On Credit And Credit Terms Accountingcoach




Analyze And Record Transactions For The Sale Of Merchandise Using The Perpetual Inventory System Principles Of Accounting Volume 1 Financial Accounting



3




Sales On Credit And Credit Terms Accountingcoach




Inventory Discounts Accounting In Focus




Acg21 Connect Ch 4




Merchandising Activities Prezentaciya Onlajn
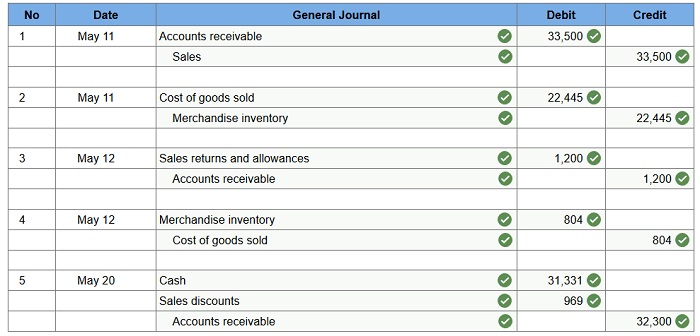



Connect Financial Accounting Chapter 4 Ask Assignment Help




Inventory Discounts Accounting In Focus



7 3 Analyze And Journalize Transactions Using Special Journals Business Libretexts
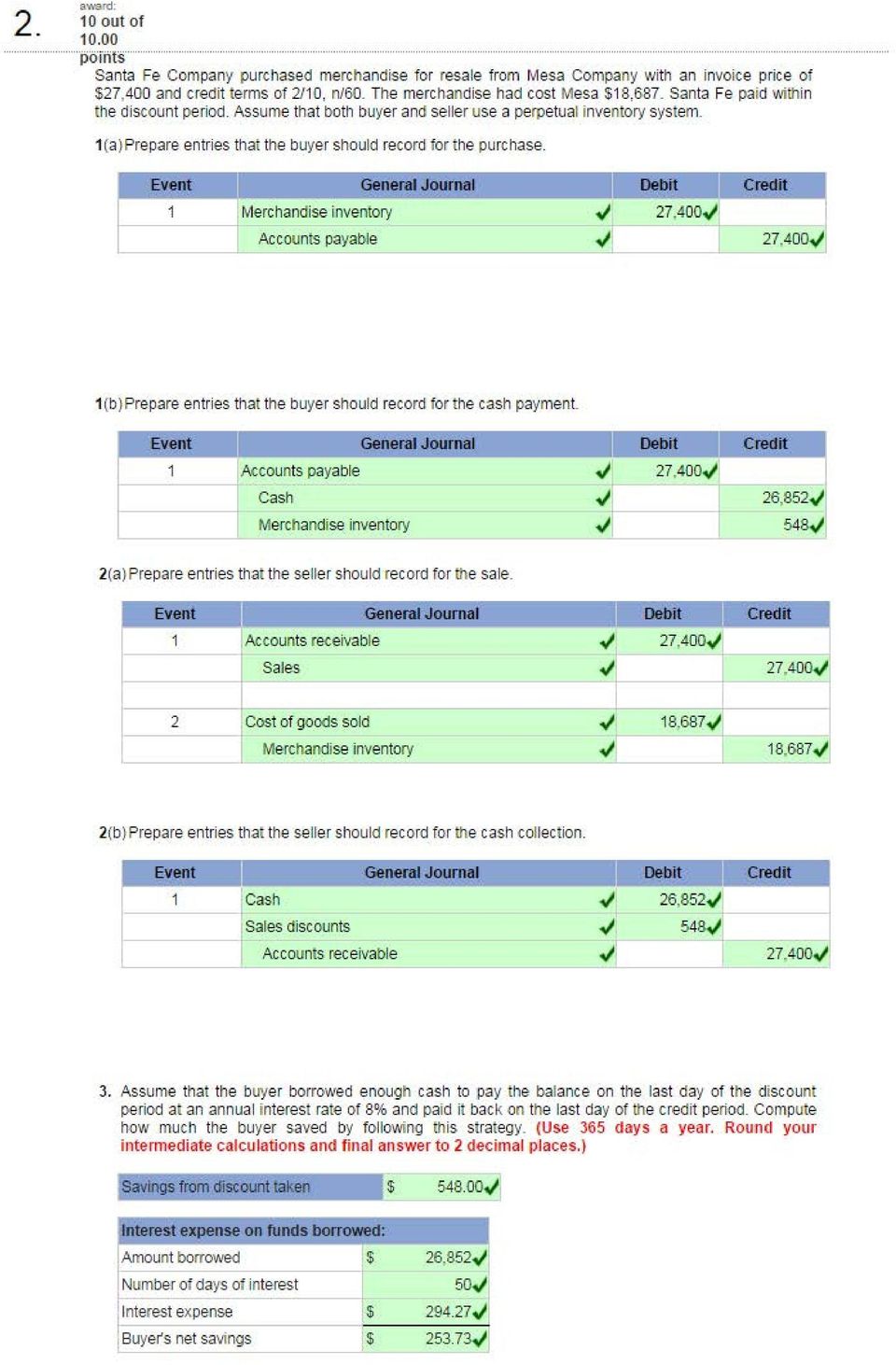



Points General Journal Debit Credit 10 Out Of Pdf Free Download




Net 30 Terms Double Entry Bookkeeping




2 10 Net 30 Understand How Trade Credits Work In Business




Treatment Of Cash Discounts Explanation Journal Entry And Example Finance Strategists
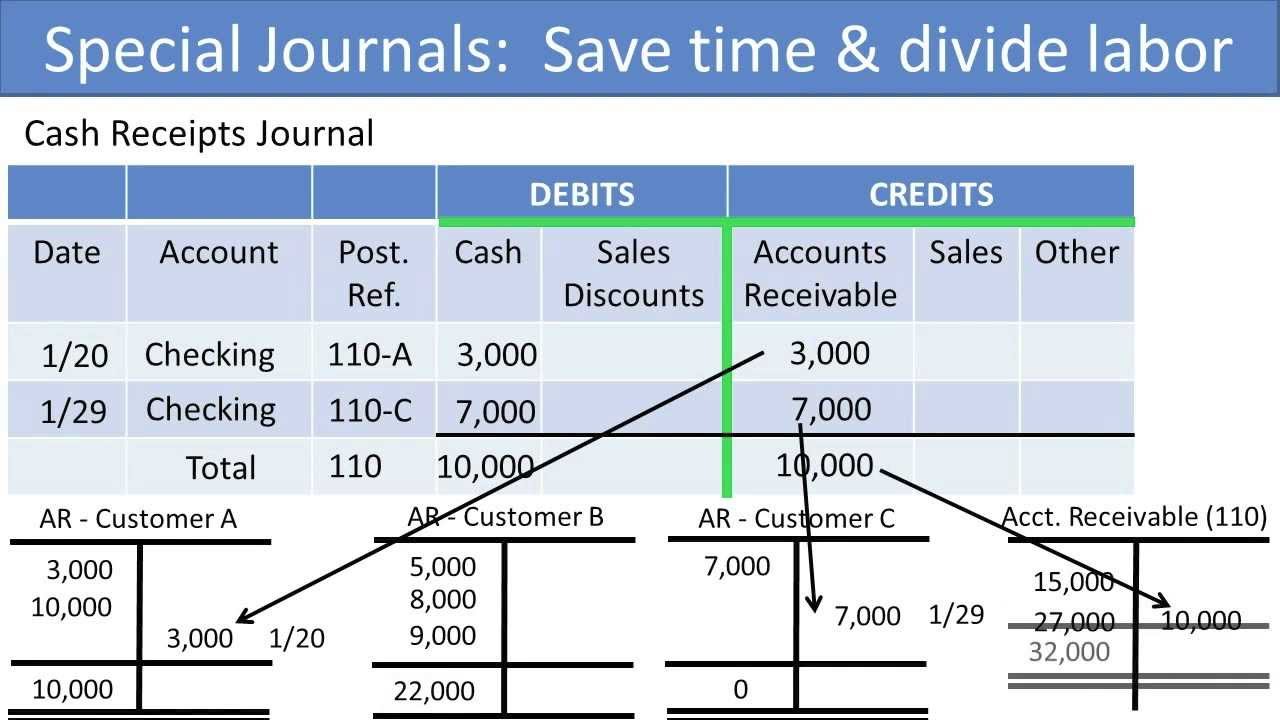



Special Journals Financial Accounting
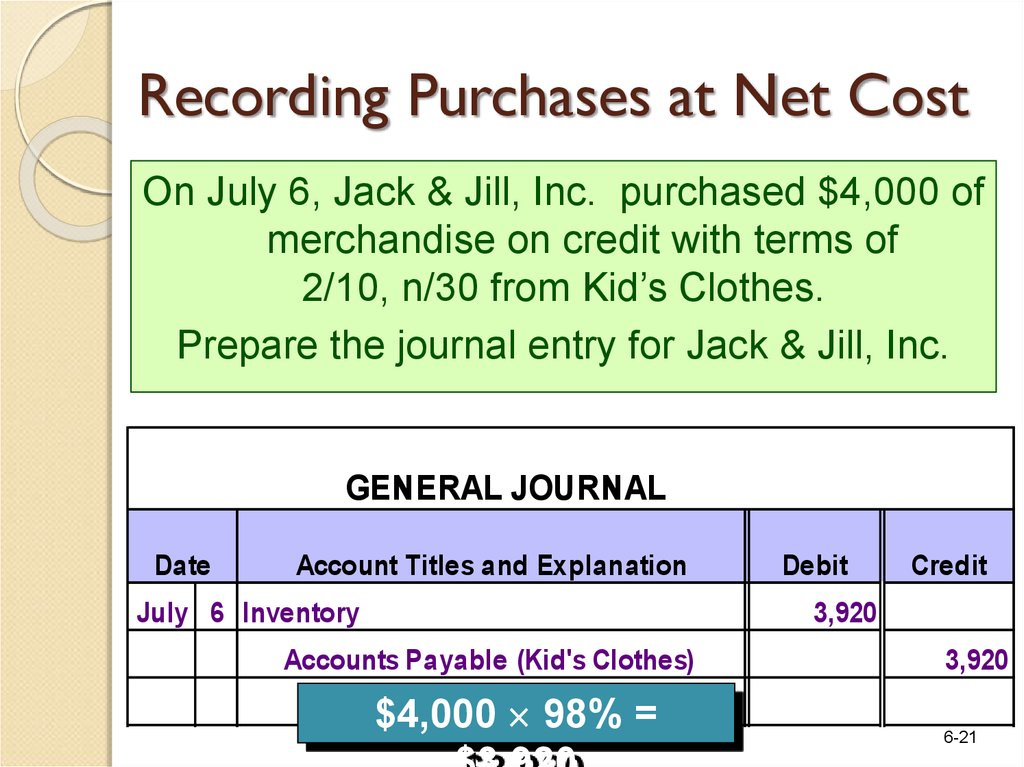



Merchandising Activities Prezentaciya Onlajn




Acg21 Connect Ch 4
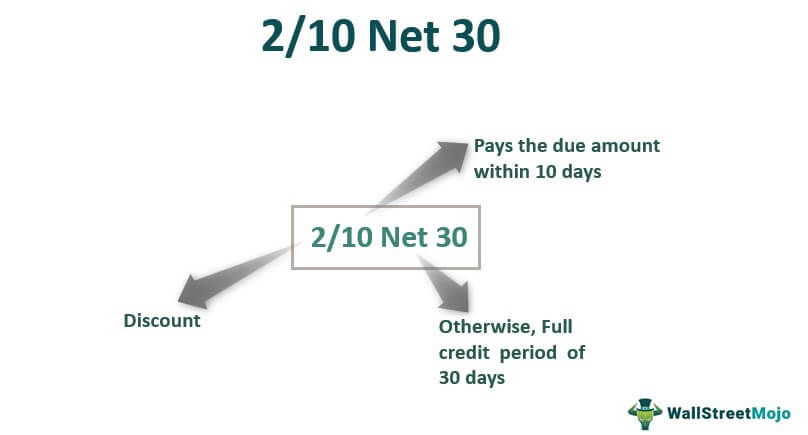



2 10 Net 30 Meaning Examples Advantages Disadvantages



2




Solved July 1 Purchased Merchandise From Boden Company For Chegg Com



Accounting For Merchandising Operations Ppt Video Online Download




On March 2 Larkspur Company Sold 901 300 Of Merchandise To Crane Company On Account Terms 3 10 1 30 Homeworklib




Wild Financial Managerial 6e Ch04




2 10 Net 30 Definition 2 10 Net 30 Calculation The Strategic Cfo




Solution When A Company Is Given Credit Accounting



1



Solved 6 Problem 4 2a Preparing Journal Entries For Chegg Com




Acg21 Connect Ch 4



2 10 Net 30 Meaning Examples Advantages Disadvantages



Answered Sales Related And Purchase Related Bartleby




Accounting For Merchandising Operations Ppt Video Online Download




Purchases Journal Definition Explanation Format Example Finance Strategists




Financial Accounting For Undergraduates 3 E Chapter 5




2 Accounting For Receivables




Glo4 01 Based On Problem 4 1a Cabela 39 S Company Lo P1 P2 Prepare Journal Entries To Record Homeworklib
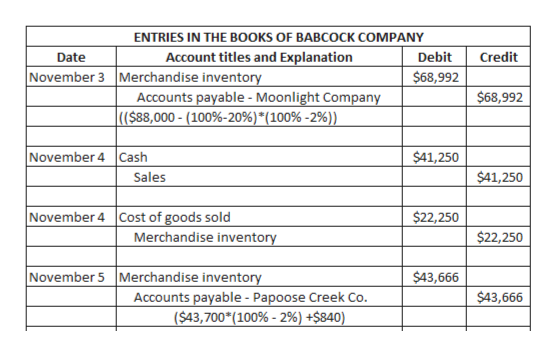



Answered Sales Related And Purchase Related Bartleby




Net Sales Accounting Video Clutch Prep




Accounting For Merchandising Businesses Ppt Download




Sales On Credit And Credit Terms Accountingcoach




What Is 2 10 N 30 Definition Meaning Example




Prepare Journal Entries To Record The Following Merchandising Transactions Of Lowe S Which Uses The Perpetual Inventory Homeworklib




Recognition Of Accounts Receivable Gross And Net Method Explanation Journal Entries And Example Accounting For Management




Solved J Sold Merchandise On Account 28 000 With Terms Chegg Com
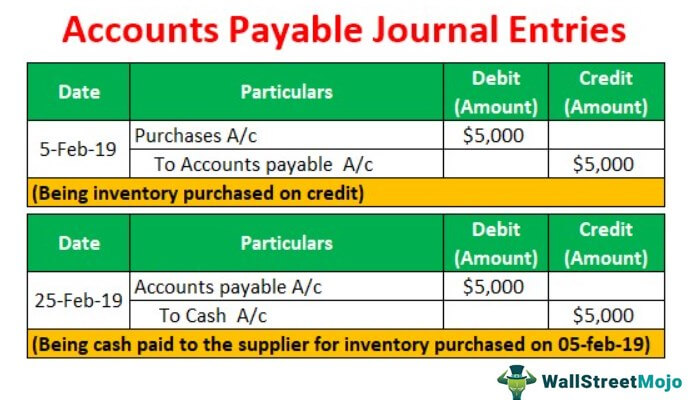



Accounts Payable Journal Entries Most Common Types Examples




Accounting For Merchandising Operations Ppt Download




Analyze Journalize And Report Current Liabilities Principles Of Accounting Volume 1 Financial Accounting



Orange Connect Another Financial Accounting Chapter 4 Continue
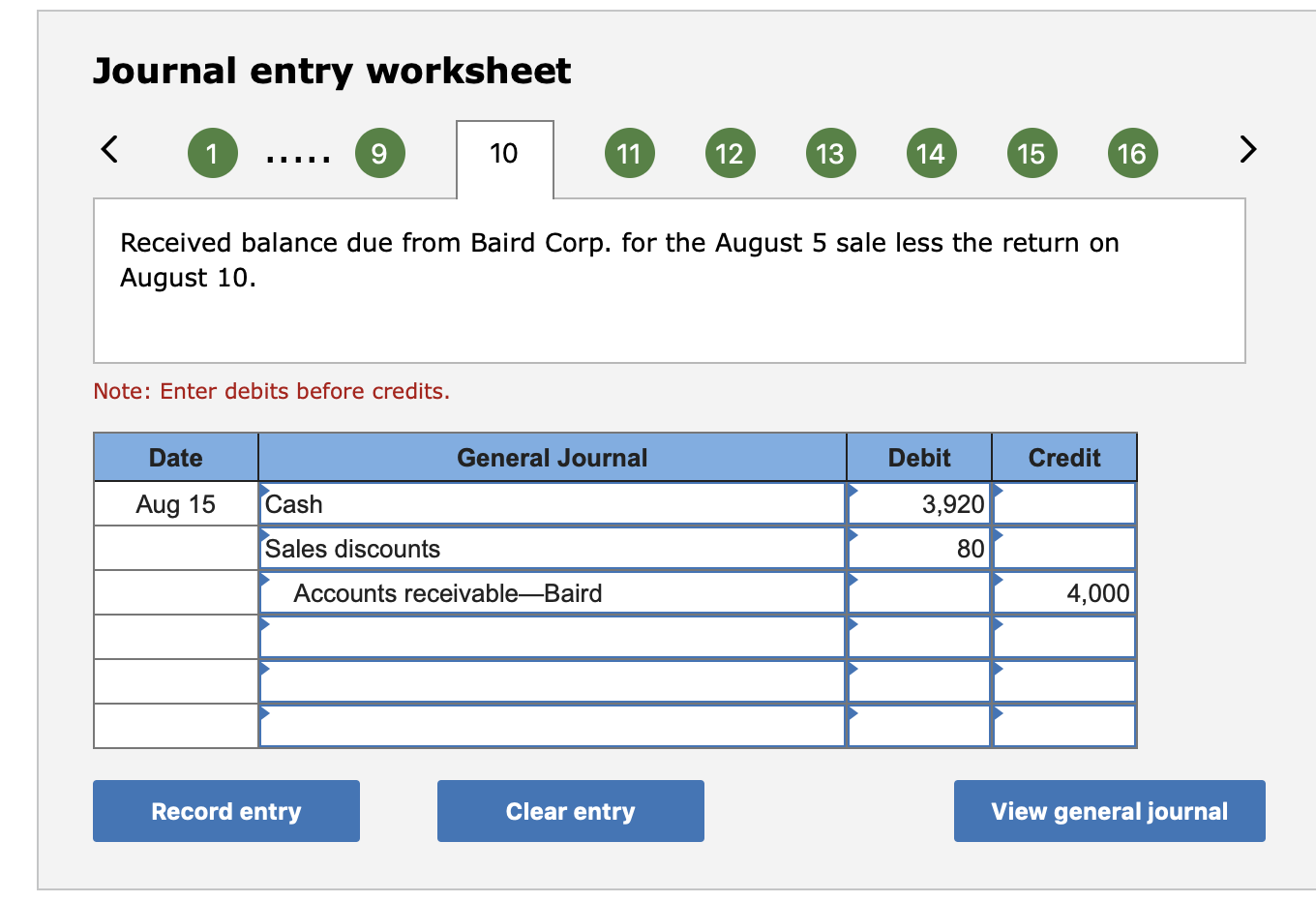



Solved Prepare Journal Entries To Record The Following Chegg Com




On Jan 3 Gourmet Cakes Sold 15 000 Of Merchandise On Account With Terms 2 10 N 30 To Jerry Hines Study Com




Gross Vs Net Method Of Accounting For Sales Discounts Youtube
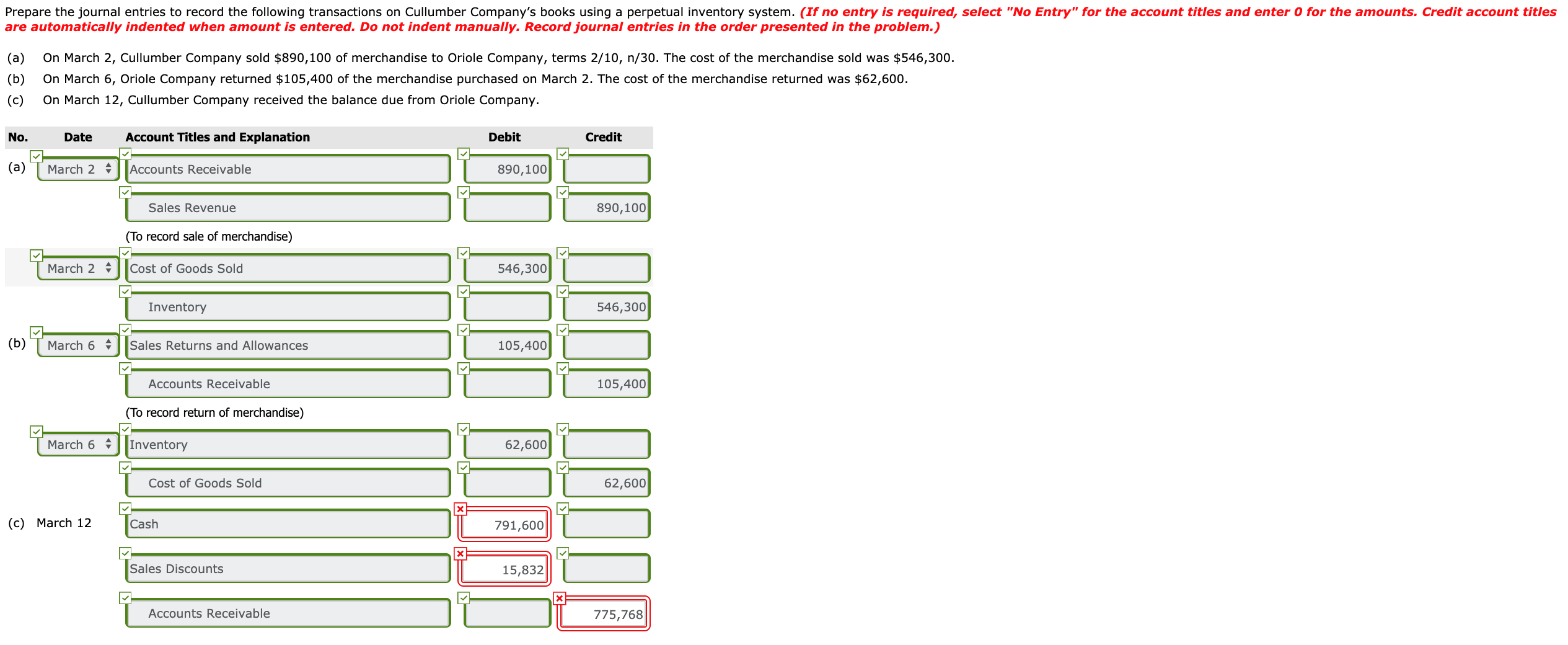



Answered Prepare The Journal Entries To Record Bartleby
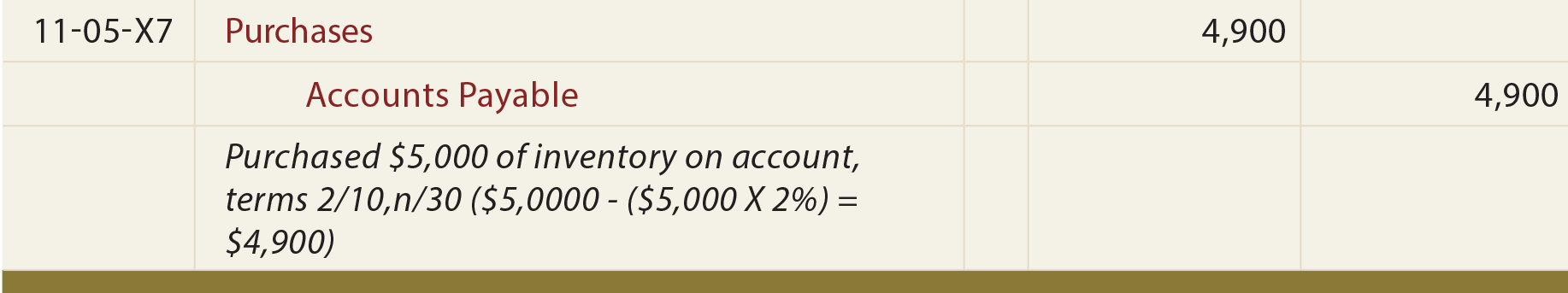



Purchases With Discount Net Principlesofaccounting Com
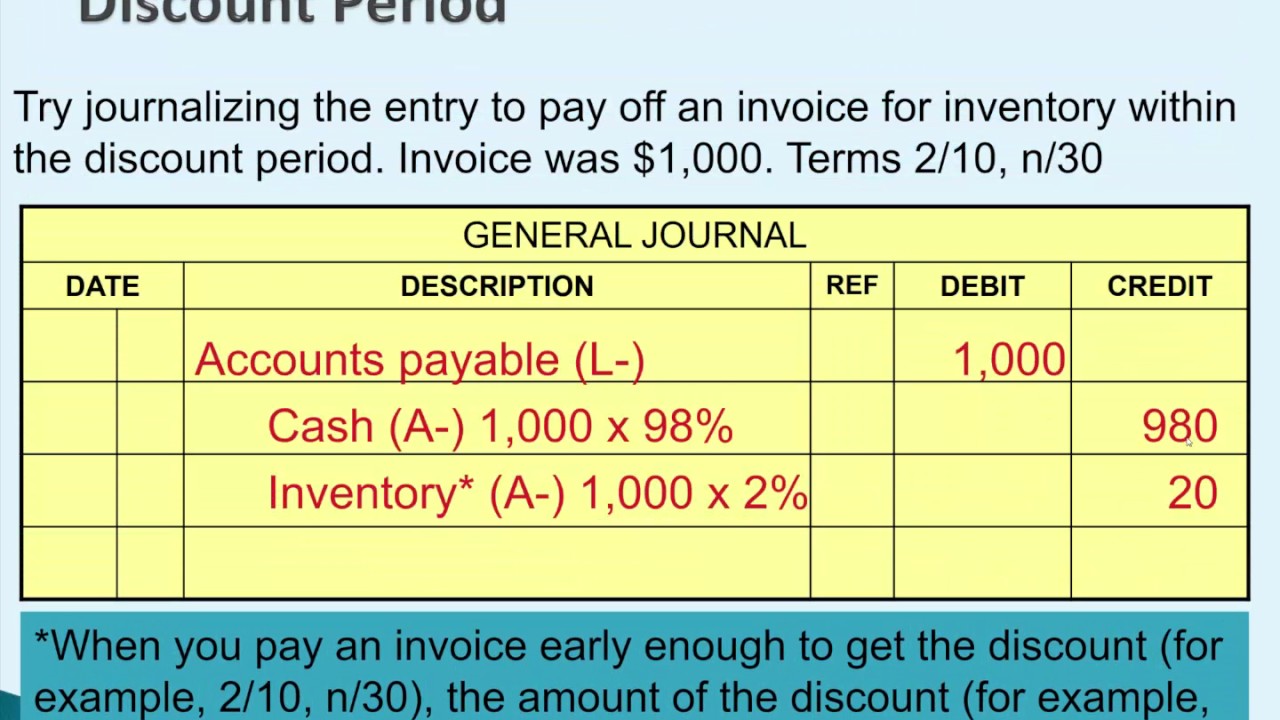



Account For Purchase Of Inventory In A Perpetual System Youtube




Journal Entry For Cash Discount Finance Strategists
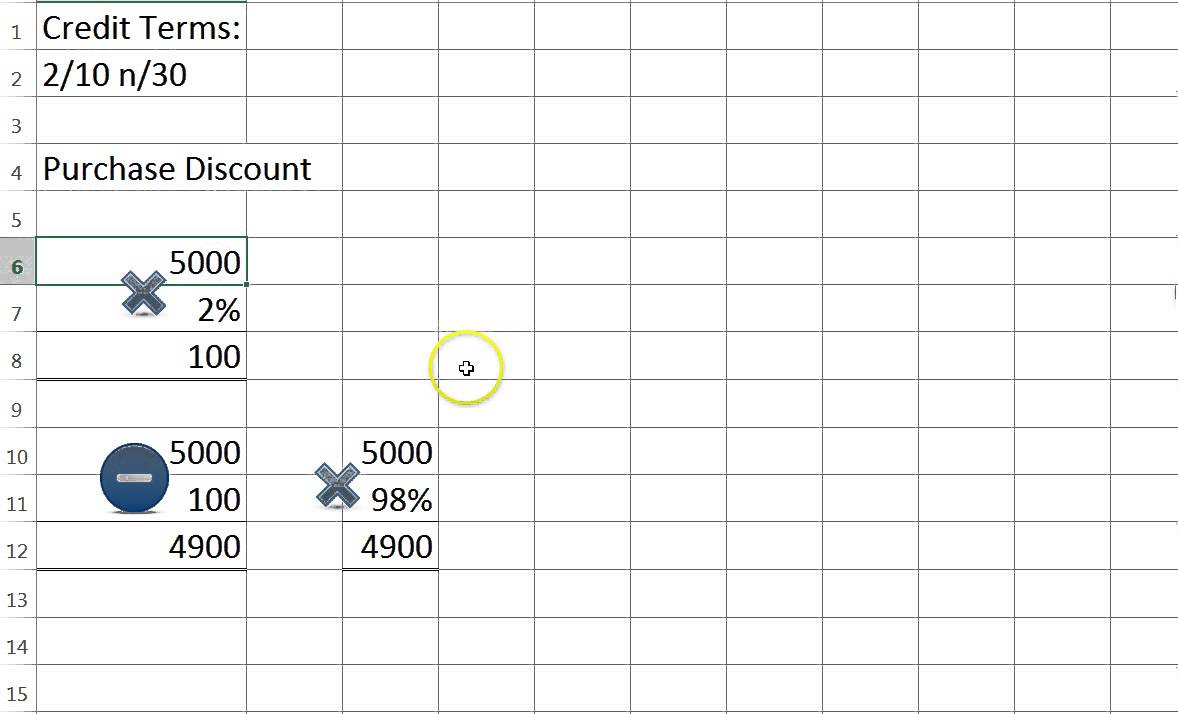



Accounting For Sales And Purchase Discounts Youtube




Chapter 05 Receivables And Sales Mc Grawhillirwin The




Early Payment Discount Reasons To Offer Accounting More



1
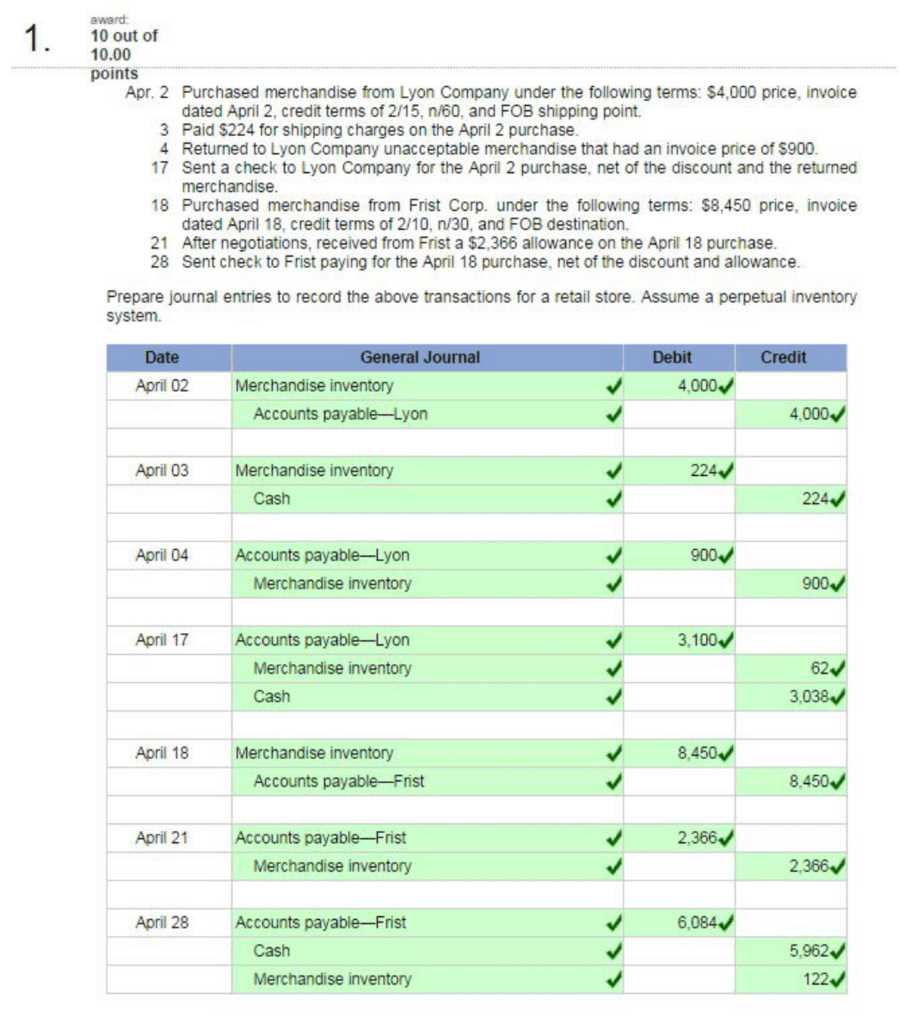



Connect Chapter 5 Homework Mgmt 026




Sales Discounts



Solved Problem 5 3 A Journal Entries For Merchandising Activities Perpetual Lo Prepare General Journal Entries To Record The Following Perpetu Course Hero




Accounting For Merchandising Activities Lecture Ppt Download




What Does 2 10 Net 30 Mean




Solved Prepare Journal Entries To Record The Following Chegg Com
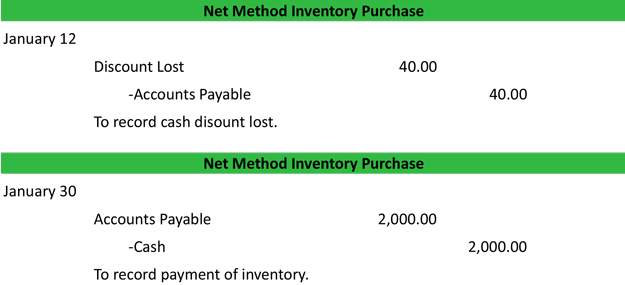



What Is The Net Method Definition Meaning Example
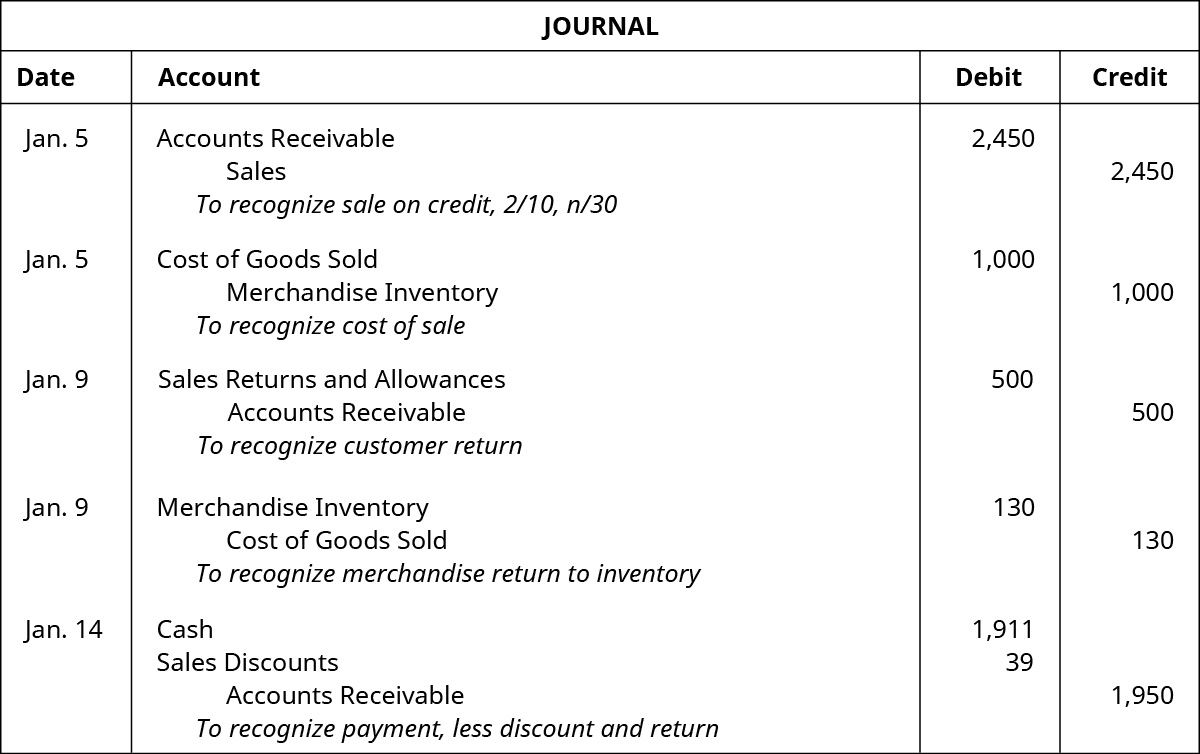



Analyze And Record Transactions For The Sale Of Merchandise Using The Perpetual Inventory System Principles Of Accounting Volume 1 Financial Accounting
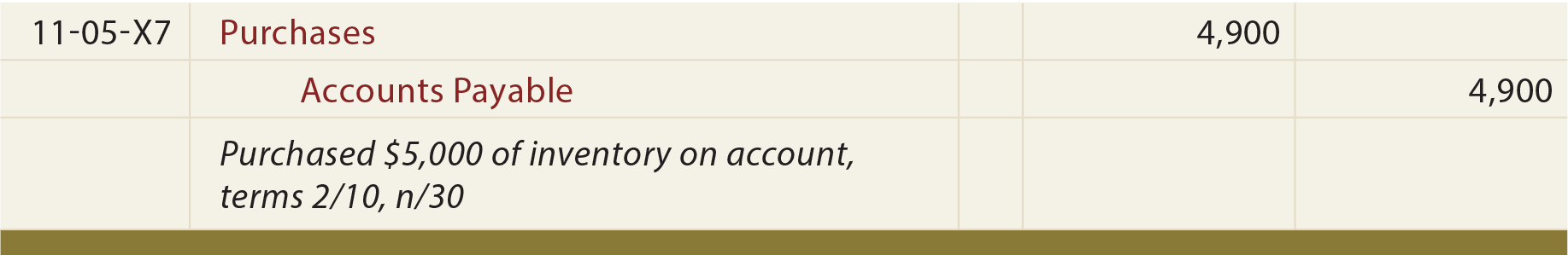



Purchase Considerations For Merchandising Businesses Principlesofaccounting Com




Fob Shipping Point Freight Prepaid Double Entry Bookkeeping



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿